Kinematic optimization for the design of a collaborative robot end-effector for tele-echography
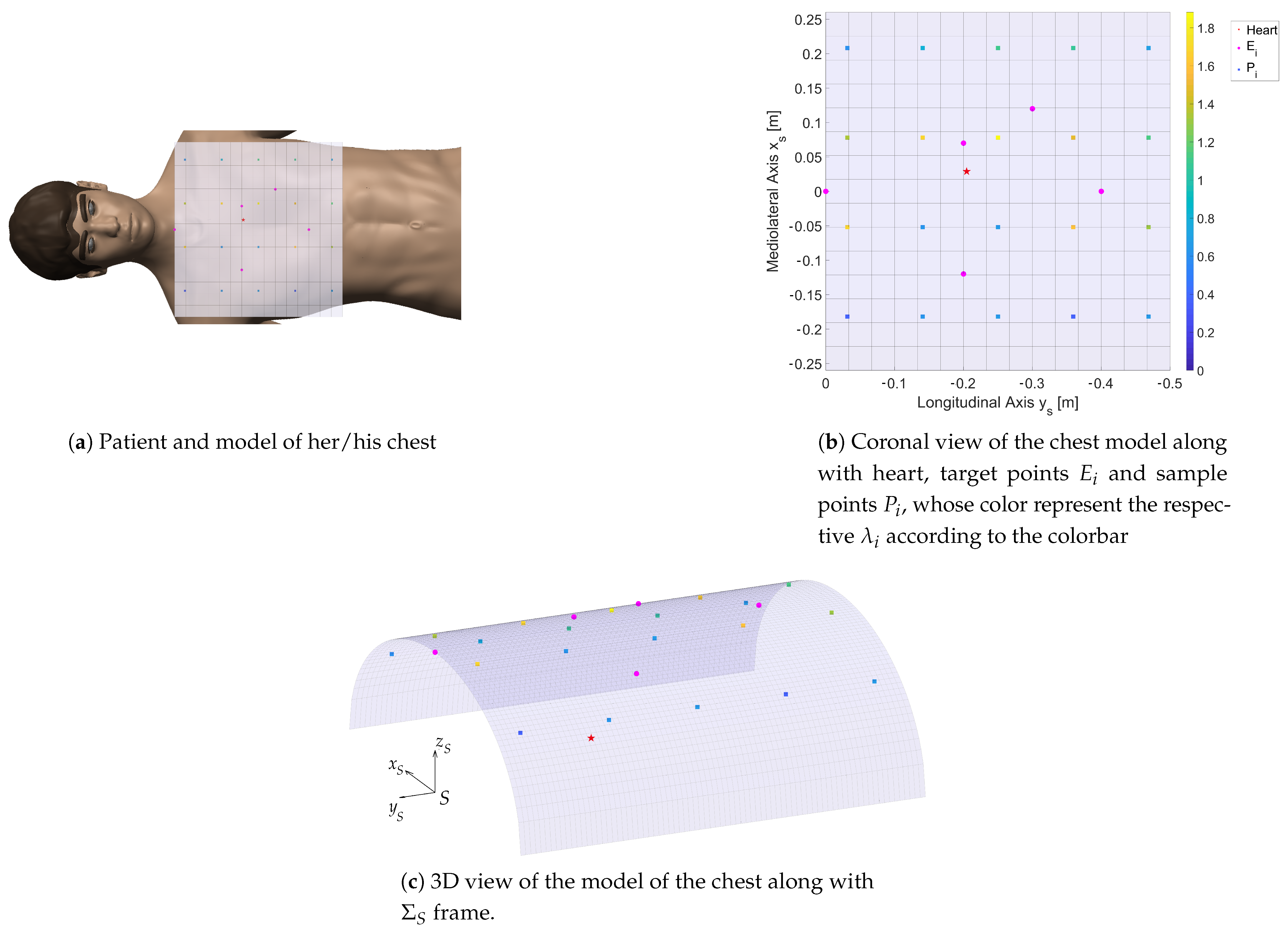
This work, developed in collaboration with the Perceptual Robotics Lab at Sant’Anna di Pisa, addresses the design of an end-effector to pair with a COTS arm to allow efficient and precise cardiac tele-ultrasonography. In particular, using an Universal Robot UR5 robotic arm, it was investigated, using a kinematic optimization based on the manipulability metric, what could be an optimal design for the application, in particular taking into consideration the effects of the introduction of additional degrees of freedom.
The results of this broad optimization problem, constrained by taking into consideration various aspects of interest for the operation, such as the position of the robot base with respect to the patient, the size of the end-effector, and the points that are more interesting to investigate during the procedure, show how an additional DoF of the end-effector improves the manipulability measure by more than 100%. This additional manipulability would guarantee a better control over the movement of the probe during the teleoperated ultrasonography.
The discussed results prove how tele-examination based on robotic state of the art technologies could safely expand from using mainly specific custom robotic arms, to more accessible commercial off the shelf arms, providing a promising solution to solve the current worsening shortage of physicians.
This work resulted in the publication of a paper that was published in Proceedings of The 3rd International Conference of IFToMM Italy, held online, 9–11 September 2020. An extended version of the paper was then published on 1 January 2021 on the journal Robotics MDPI special issue Kinematics and Robot Design III, KaRD2020. |

